-
Preface
- FAQ
-
Part I - Basics
- Basics Data Structure
- Basics Sorting
- Basics Algorithm
- Basics Misc
-
Part II - Coding
- String
-
Integer Array
-
Remove Element
-
Zero Sum Subarray
-
Subarray Sum K
-
Subarray Sum Closest
-
Recover Rotated Sorted Array
-
Product of Array Exclude Itself
-
Partition Array
-
First Missing Positive
-
2 Sum
-
3 Sum
-
3 Sum Closest
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array II
-
Merge Sorted Array
-
Merge Sorted Array II
-
Median
-
Partition Array by Odd and Even
-
Kth Largest Element
-
Remove Element
-
Binary Search
-
First Position of Target
-
Search Insert Position
-
Search for a Range
-
First Bad Version
-
Search a 2D Matrix
-
Search a 2D Matrix II
-
Find Peak Element
-
Search in Rotated Sorted Array
-
Search in Rotated Sorted Array II
-
Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array
-
Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array II
-
Median of two Sorted Arrays
-
Sqrt x
-
Wood Cut
-
First Position of Target
-
Math and Bit Manipulation
-
Single Number
-
Single Number II
-
Single Number III
-
O1 Check Power of 2
-
Convert Integer A to Integer B
-
Factorial Trailing Zeroes
-
Unique Binary Search Trees
-
Update Bits
-
Fast Power
-
Hash Function
-
Happy Number
-
Count 1 in Binary
-
Fibonacci
-
A plus B Problem
-
Print Numbers by Recursion
-
Majority Number
-
Majority Number II
-
Majority Number III
-
Digit Counts
-
Ugly Number
-
Plus One
-
Palindrome Number
-
Task Scheduler
-
Single Number
-
Linked List
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
-
Remove Duplicates from Unsorted List
-
Partition List
-
Add Two Numbers
-
Two Lists Sum Advanced
-
Remove Nth Node From End of List
-
Linked List Cycle
-
Linked List Cycle II
-
Reverse Linked List
-
Reverse Linked List II
-
Merge Two Sorted Lists
-
Merge k Sorted Lists
-
Reorder List
-
Copy List with Random Pointer
-
Sort List
-
Insertion Sort List
-
Palindrome Linked List
-
LRU Cache
-
Rotate List
-
Swap Nodes in Pairs
-
Remove Linked List Elements
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
-
Binary Tree
-
Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
-
Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
-
Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
-
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
-
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
-
Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
-
Balanced Binary Tree
-
Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum
-
Lowest Common Ancestor
-
Invert Binary Tree
-
Diameter of a Binary Tree
-
Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
-
Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
-
Subtree
-
Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
-
Binary Tree Serialization
-
Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
- Binary Search Tree
- Exhaustive Search
-
Dynamic Programming
-
Triangle
-
Backpack
-
Backpack II
-
Minimum Path Sum
-
Unique Paths
-
Unique Paths II
-
Climbing Stairs
-
Jump Game
-
Word Break
-
Longest Increasing Subsequence
-
Palindrome Partitioning II
-
Longest Common Subsequence
-
Edit Distance
-
Jump Game II
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV
-
Distinct Subsequences
-
Interleaving String
-
Maximum Subarray
-
Maximum Subarray II
-
Longest Increasing Continuous subsequence
-
Longest Increasing Continuous subsequence II
-
Maximal Square
-
Triangle
- Graph
- Data Structure
- Big Data
- Problem Misc
-
Part III - Contest
- Google APAC
- Microsoft
- Appendix I Interview and Resume
-
Tags
Binary Tree - 二叉树
二叉树是每个节点最多有两个子树的树结构,子树有左右之分,二叉树常被用于实现二叉查找树和二叉堆。
二叉树的第i层至多有 个结点;深度为k的二叉树至多有 个结点;对任何一棵二叉树T,如果其终端结点数为 , 度为2的结点数为 , 则 。因为度为1的节点对度为0的节点数目不会有影响,而每增加一个度为2的节点总的来说则会相应增加一个度为0的节点。
一棵深度为 , 且有 个节点称之为满二叉树;深度为 ,有 个节点的二叉树,当且仅当其每一个节点都与深度为 的满二叉树中序号为 至 的节点对应时,称之为完全二叉树。完全二叉树中重在节点标号对应。
编程实现
Python
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.left, self.right = None, None
 copy
copyC++
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
 copy
copyJava
public class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left, right;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
 copy
copy树的遍历
从二叉树的根节点出发,节点的遍历分为三个主要步骤:对当前节点进行操作(称为“访问”节点,或者根节点)、遍历左边子节点、遍历右边子节点。访问节点顺序的不同也就形成了不同的遍历方式。需要注意的是树的遍历通常使用递归的方法进行理解和实现,在访问元素时也需要使用递归的思想去理解。实际实现中对于前序和中序遍历可尝试使用递归实现。
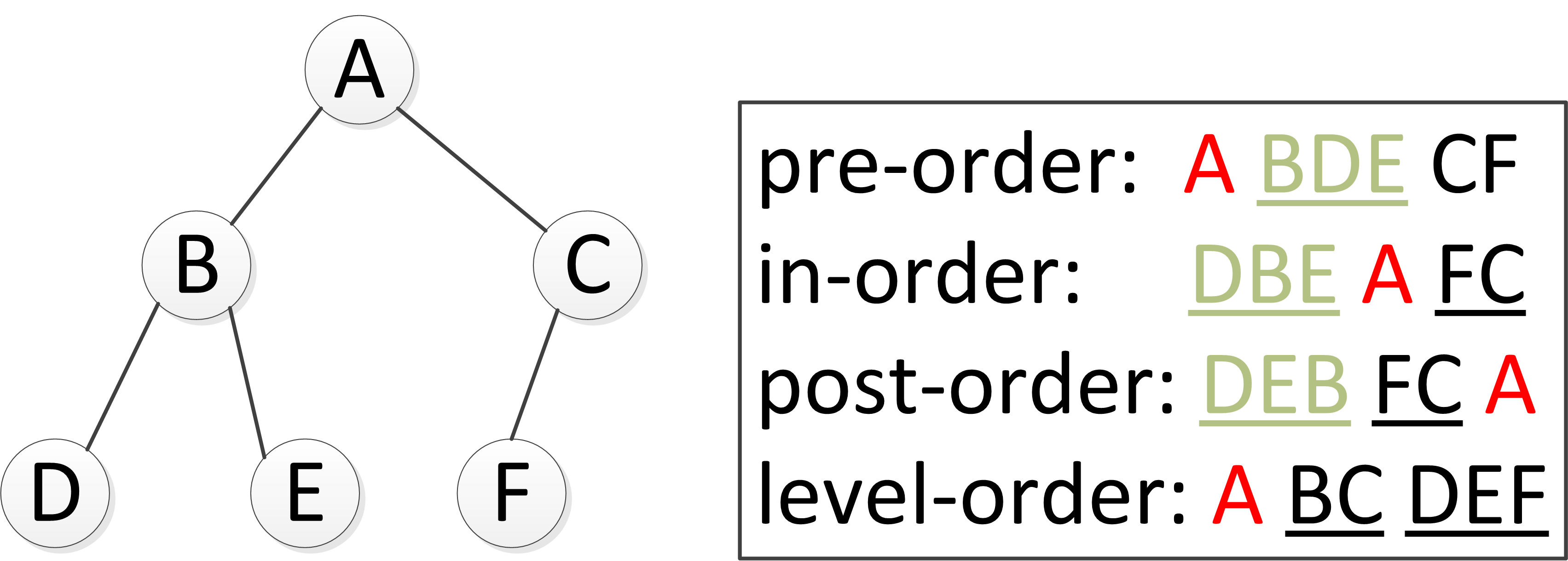
按照访问根元素(当前元素)的前后顺序,遍历方式可划分为如下几种:
- 深度优先:先访问子节点,再访问父节点,最后访问第二个子节点。根据根节点相对于左右子节点的访问先后顺序又可细分为以下三种方式。
- 前序(pre-order):先根后左再右
- 中序(in-order):先左后根再右
- 后序(post-order):先左后右再根
- 广度优先:先访问根节点,沿着树的宽度遍历子节点,直到所有节点均被访问为止。
如下图所示,遍历顺序在右侧框中,红色A为根节点。使用递归和整体的思想去分析遍历顺序较为清晰。
二叉树的广度优先遍历和树的前序/中序/后序遍历不太一样,前/中/后序遍历使用递归,也就是栈的思想对二叉树进行遍历,广度优先一般使用队列的思想对二叉树进行遍历。
如果已知中序遍历和前序遍历或者后序遍历,那么就可以完全恢复出原二叉树结构。其中最为关键的是前序遍历中第一个一定是根,而后序遍历最后一个一定是根,中序遍历在得知根节点后又可进一步递归得知左右子树的根节点。但是这种方法也是有适用范围的:元素不能重复!否则无法完成定位。
Python
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.left, self.right = None, None
class Traversal(object):
def __init__(self):
self.traverse_path = list()
def preorder(self, root):
if root:
self.traverse_path.append(root.val)
self.preorder(root.left)
self.preorder(root.right)
def inorder(self,root):
if root:
self.inorder(root.left)
self.traverse_path.append(root.val)
self.inorder(root.right)
def postorder(self,root):
if root:
self.postorder(root.left)
self.postorder(root.right)
self.traverse_path.append(root.val)
 copy
copy树类题的复杂度分析
对树相关的题进行复杂度分析时可统计对每个节点被访问的次数,进而求得总的时间复杂度。
Binary Search Tree - 二叉查找树
一颗二叉查找树(BST)**是一颗二叉树,其中每个节点都含有一个可进行比较的键及相应的值,且每个节点的键都大于等于左子树中的任意节点的键,而小于右子树中的任意节点的键**。
使用中序遍历可得到有序数组,这是二叉查找树的又一个重要特征。
二叉查找树使用的每个节点含有两个链接,它是将链表插入的灵活性和有序数组查找的高效性结合起来的高效符号表实现。
