-
Preface
- FAQ
-
Part I - Basics
- Basics Data Structure
- Basics Sorting
- Basics Algorithm
- Basics Misc
-
Part II - Coding
- String
-
Integer Array
-
Remove Element
-
Zero Sum Subarray
-
Subarray Sum K
-
Subarray Sum Closest
-
Recover Rotated Sorted Array
-
Product of Array Exclude Itself
-
Partition Array
-
First Missing Positive
-
2 Sum
-
3 Sum
-
3 Sum Closest
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array II
-
Merge Sorted Array
-
Merge Sorted Array II
-
Median
-
Partition Array by Odd and Even
-
Kth Largest Element
-
Remove Element
-
Binary Search
-
First Position of Target
-
Search Insert Position
-
Search for a Range
-
First Bad Version
-
Search a 2D Matrix
-
Search a 2D Matrix II
-
Find Peak Element
-
Search in Rotated Sorted Array
-
Search in Rotated Sorted Array II
-
Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array
-
Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array II
-
Median of two Sorted Arrays
-
Sqrt x
-
Wood Cut
-
First Position of Target
-
Math and Bit Manipulation
-
Single Number
-
Single Number II
-
Single Number III
-
O1 Check Power of 2
-
Convert Integer A to Integer B
-
Factorial Trailing Zeroes
-
Unique Binary Search Trees
-
Update Bits
-
Fast Power
-
Hash Function
-
Happy Number
-
Count 1 in Binary
-
Fibonacci
-
A plus B Problem
-
Print Numbers by Recursion
-
Majority Number
-
Majority Number II
-
Majority Number III
-
Digit Counts
-
Ugly Number
-
Plus One
-
Palindrome Number
-
Task Scheduler
-
Single Number
-
Linked List
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
-
Remove Duplicates from Unsorted List
-
Partition List
-
Add Two Numbers
-
Two Lists Sum Advanced
-
Remove Nth Node From End of List
-
Linked List Cycle
-
Linked List Cycle II
-
Reverse Linked List
-
Reverse Linked List II
-
Merge Two Sorted Lists
-
Merge k Sorted Lists
-
Reorder List
-
Copy List with Random Pointer
-
Sort List
-
Insertion Sort List
-
Palindrome Linked List
-
LRU Cache
-
Rotate List
-
Swap Nodes in Pairs
-
Remove Linked List Elements
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
-
Binary Tree
-
Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
-
Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
-
Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
-
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
-
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
-
Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
-
Balanced Binary Tree
-
Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum
-
Lowest Common Ancestor
-
Invert Binary Tree
-
Diameter of a Binary Tree
-
Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
-
Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
-
Subtree
-
Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
-
Binary Tree Serialization
-
Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
- Binary Search Tree
- Exhaustive Search
-
Dynamic Programming
-
Triangle
-
Backpack
-
Backpack II
-
Minimum Path Sum
-
Unique Paths
-
Unique Paths II
-
Climbing Stairs
-
Jump Game
-
Word Break
-
Longest Increasing Subsequence
-
Palindrome Partitioning II
-
Longest Common Subsequence
-
Edit Distance
-
Jump Game II
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV
-
Distinct Subsequences
-
Interleaving String
-
Maximum Subarray
-
Maximum Subarray II
-
Longest Increasing Continuous subsequence
-
Longest Increasing Continuous subsequence II
-
Maximal Square
-
Triangle
- Graph
- Data Structure
- Big Data
- Problem Misc
-
Part III - Contest
- Google APAC
- Microsoft
- Appendix I Interview and Resume
-
Tags
Insertion Sort List
Tags: Linked List, Sort, Medium
Question
- leetcode: Insertion Sort List
- lintcode: Insertion Sort List
Problem Statement
Sort a linked list using insertion sort.

A graphical example of insertion sort. The partial sorted list (black)
initially contains only the first element in the list.
With each iteration one element (red) is removed from the input data and
inserted in-place into the sorted list
Algorithm of Insertion Sort:
- Insertion sort iterates, consuming one input element each repetition, and growing a sorted output list.
- At each iteration, insertion sort removes one element from the input data, finds the location it belongs within the sorted list, and inserts it there.
- It repeats until no input elements remain.
Example 1:
**Input:** 4->2->1->3
**Output:** 1->2->3->4
 copy
copyExample 2:
**Input:** -1->5->3->4->0
**Output:** -1->0->3->4->5
 copy
copy题解1 - 从首到尾遍历
插入排序常见的实现是针对数组的,如前几章总的的 Insertion Sort,但这道题中的排序的数据结构为单向链表,故无法再从后往前遍历比较值的大小了。好在天无绝人之路,我们还可以从前往后依次遍历比较和交换。
由于排序后头节点不一定,故需要引入 dummy 大法,并以此节点的next作为最后返回结果的头节点,返回的链表从dummy->next这里开始构建。首先我们每次都从dummy->next开始遍历,依次和上一轮处理到的节点的值进行比较,直至找到不小于上一轮节点值的节点为止,随后将上一轮节点插入到当前遍历的节点之前,依此类推。文字描述起来可能比较模糊,大家可以结合以下的代码在纸上分析下。
Python
"""
Definition of ListNode
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
"""
class Solution:
"""
@param head: The first node of linked list.
@return: The head of linked list.
"""
def insertionSortList(self, head):
dummy = ListNode(0)
cur = head
while cur is not None:
pre = dummy
while pre.next is not None and pre.next.val < cur.val:
pre = pre.next
temp = cur.next
cur.next = pre.next
pre.next = cur
cur = temp
return dummy.next
 copy
copyC++
/**
* Definition of ListNode
* class ListNode {
* public:
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int val) {
* this->val = val;
* this->next = NULL;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public:
/**
* @param head: The first node of linked list.
* @return: The head of linked list.
*/
ListNode *insertionSortList(ListNode *head) {
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode *cur = head;
while (cur != NULL) {
ListNode *pre = dummy;
while (pre->next != NULL && pre->next->val < cur->val) {
pre = pre->next;
}
ListNode *temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre->next;
pre->next = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
 copy
copyJava
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode pre = dummy;
while (pre.next != null && pre.next.val < cur.val) {
pre = pre.next;
}
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre.next;
pre.next = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
 copy
copy源码分析
- 新建 dummy 节点,用以处理最终返回结果中头节点不定的情况。
- 以
cur表示当前正在处理的节点,在从 dummy 开始遍历前保存cur的下一个节点作为下一轮的cur. - 以
pre作为遍历节点,直到找到不小于cur值的节点为止。 - 将
pre的下一个节点pre->next链接到cur->next上,cur链接到pre->next, 最后将cur指向下一个节点。 - 返回
dummy->next最为最终头节点。
Python 的实现在 lintcode 上会提示 TLE, leetcode 上勉强通过,这里需要注意的是采用if A is not None:的效率要比if A:高,不然 leetcode 上也过不了。具体原因可参考 Stack Overflow 上的讨论。
复杂度分析
最好情况:原链表已经逆序,每得到一个新节点仅需要一次比较, 时间复杂度为 , 使用了 dummy 和 pre, 空间复杂度近似为 .
最坏情况:原链表正好升序,由于是单向链表只能从前往后依次遍历,交换和比较次数均为 , 总的时间复杂度近似为 , 空间复杂度同上,近似为 .
题解2 - 优化有序链表
从题解1的复杂度分析可以看出其在最好情况下时间复杂度都为 ,这显然是需要优化的。 仔细观察可发现最好情况下的比较次数 是可以优化到 的。思路自然就是先判断链表是否有序,仅对降序的部分进行处理。优化之后的代码就没题解1那么容易写对了,建议画个图自行纸上分析下。
Python
"""
Definition of ListNode
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
"""
class Solution:
"""
@param head: The first node of linked list.
@return: The head of linked list.
"""
def insertionSortList(self, head):
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
cur = head
while cur is not None:
if cur.next is not None and cur.next.val < cur.val:
# find insert position for smaller(cur->next)
pre = dummy
while pre.next is not None and pre.next.val < cur.next.val:
pre = pre.next
# insert cur->next after pre
temp = pre.next
pre.next = cur.next
cur.next = cur.next.next
pre.next.next = temp
else:
cur = cur.next
return dummy.next
 copy
copyC++
/**
* Definition of ListNode
* class ListNode {
* public:
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int val) {
* this->val = val;
* this->next = NULL;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public:
/**
* @param head: The first node of linked list.
* @return: The head of linked list.
*/
ListNode *insertionSortList(ListNode *head) {
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy->next = head;
ListNode *cur = head;
while (cur != NULL) {
if (cur->next != NULL && cur->next->val < cur->val) {
ListNode *pre = dummy;
// find insert position for smaller(cur->next)
while (pre->next != NULL && pre->next->val <= cur->next->val) {
pre = pre->next;
}
// insert cur->next after pre
ListNode *temp = pre->next;
pre->next = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
pre->next->next = temp;
} else {
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
 copy
copyJava
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.next != null && cur.next.val < cur.val) {
// find insert position for smaller(cur->next)
ListNode pre = dummy;
while (pre.next != null && pre.next.val < cur.next.val) {
pre = pre.next;
}
// insert cur->next after pre
ListNode temp = pre.next;
pre.next = cur.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
pre.next.next = temp;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
 copy
copy源码分析
- 新建 dummy 节点并将其
next指向head - 分情况讨论,仅需要处理逆序部分。
- 由于已经确认链表逆序,故仅需将较小值(
cur->next而不是cur)的节点插入到链表的合适位置。 - 将
cur->next插入到pre之后,这里需要四个步骤,需要特别小心!
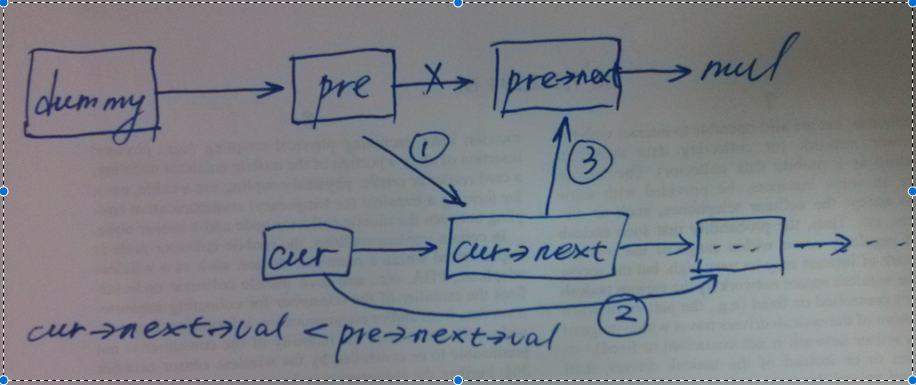
如上图所示,将cur->next插入到pre节点后大致分为3个步骤。
复杂度分析
最好情况下时间复杂度降至 , 其他同题解1.
