-
Preface
- FAQ
-
Part I - Basics
- Basics Data Structure
- Basics Sorting
- Basics Algorithm
- Basics Misc
-
Part II - Coding
- String
-
Integer Array
-
Remove Element
-
Zero Sum Subarray
-
Subarray Sum K
-
Subarray Sum Closest
-
Recover Rotated Sorted Array
-
Product of Array Exclude Itself
-
Partition Array
-
First Missing Positive
-
2 Sum
-
3 Sum
-
3 Sum Closest
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array II
-
Merge Sorted Array
-
Merge Sorted Array II
-
Median
-
Partition Array by Odd and Even
-
Kth Largest Element
-
Remove Element
-
Binary Search
-
First Position of Target
-
Search Insert Position
-
Search for a Range
-
First Bad Version
-
Search a 2D Matrix
-
Search a 2D Matrix II
-
Find Peak Element
-
Search in Rotated Sorted Array
-
Search in Rotated Sorted Array II
-
Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array
-
Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array II
-
Median of two Sorted Arrays
-
Sqrt x
-
Wood Cut
-
First Position of Target
-
Math and Bit Manipulation
-
Single Number
-
Single Number II
-
Single Number III
-
O1 Check Power of 2
-
Convert Integer A to Integer B
-
Factorial Trailing Zeroes
-
Unique Binary Search Trees
-
Update Bits
-
Fast Power
-
Hash Function
-
Happy Number
-
Count 1 in Binary
-
Fibonacci
-
A plus B Problem
-
Print Numbers by Recursion
-
Majority Number
-
Majority Number II
-
Majority Number III
-
Digit Counts
-
Ugly Number
-
Plus One
-
Palindrome Number
-
Task Scheduler
-
Single Number
-
Linked List
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
-
Remove Duplicates from Unsorted List
-
Partition List
-
Add Two Numbers
-
Two Lists Sum Advanced
-
Remove Nth Node From End of List
-
Linked List Cycle
-
Linked List Cycle II
-
Reverse Linked List
-
Reverse Linked List II
-
Merge Two Sorted Lists
-
Merge k Sorted Lists
-
Reorder List
-
Copy List with Random Pointer
-
Sort List
-
Insertion Sort List
-
Palindrome Linked List
-
LRU Cache
-
Rotate List
-
Swap Nodes in Pairs
-
Remove Linked List Elements
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
-
Binary Tree
-
Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
-
Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
-
Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
-
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
-
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
-
Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
-
Balanced Binary Tree
-
Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum
-
Lowest Common Ancestor
-
Invert Binary Tree
-
Diameter of a Binary Tree
-
Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
-
Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
-
Subtree
-
Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
-
Binary Tree Serialization
-
Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
- Binary Search Tree
- Exhaustive Search
-
Dynamic Programming
-
Triangle
-
Backpack
-
Backpack II
-
Minimum Path Sum
-
Unique Paths
-
Unique Paths II
-
Climbing Stairs
-
Jump Game
-
Word Break
-
Longest Increasing Subsequence
-
Palindrome Partitioning II
-
Longest Common Subsequence
-
Edit Distance
-
Jump Game II
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV
-
Distinct Subsequences
-
Interleaving String
-
Maximum Subarray
-
Maximum Subarray II
-
Longest Increasing Continuous subsequence
-
Longest Increasing Continuous subsequence II
-
Maximal Square
-
Triangle
- Graph
- Data Structure
- Big Data
- Problem Misc
-
Part III - Contest
- Google APAC
- Microsoft
- Appendix I Interview and Resume
-
Tags
Bipartial Graph - Part I - 二分图一•二分图判定
Question
Problem Statement
时间限制:10000ms
单点时限:1000ms
内存限制:256MB
描述
大家好,我是小Hi和小Ho的小伙伴Nettle,从这个星期开始由我来完成我们的Weekly。
新年回家,又到了一年一度大龄剩男剩女的相亲时间。Nettle去姑姑家玩的时候看到了一张姑姑写的相亲情况表,上面都是姑姑介绍相亲的剩男剩女们。每行有2个名字, 表示这两个人有一场相亲。由于姑姑年龄比较大了记性不是太好,加上相亲的人很多,所以姑姑一时也想不起来其中有些人的性别。因此她拜托我检查一下相亲表里面有没有错误 的记录,即是否把两个同性安排了相亲。
OK,让我们愉快的暴力搜索吧!
才怪咧。
对于拿到的相亲情况表,我们不妨将其转化成一个图。将每一个人作为一个点**(编号1..N)**,若两个人之间有一场相亲,则在对应的点之间连接一条无向边。(如下图)
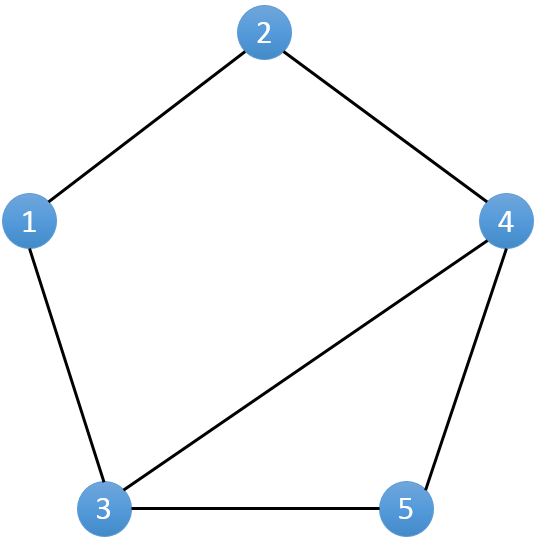
因为相亲总是在男女之间进行的,所以每一条边的两边对应的人总是不同性别。假设表示男性的节点染成白色,女性的节点染色黑色。对于得到的无向图来说,即每一条边的两端 一定是一白一黑。如果存在一条边两端同为白色或者黑色,则表示这一条边所表示的记录有误。
由于我们并不知道每个人的性别,我们的问题就转化为判定是否存在一个合理的染色方案,使得我们所建立的无向图满足每一条边两端的顶点颜色都不相同。
那么,我们不妨将所有的点初始为未染色的状态。随机选择一个点,将其染成白色。再以它为起点,将所有相邻的点染成黑色。再以这些黑色的点为起点,将所有与其相邻未染色 的点染成白色。不断重复直到整个图都染色完成。(如下图)
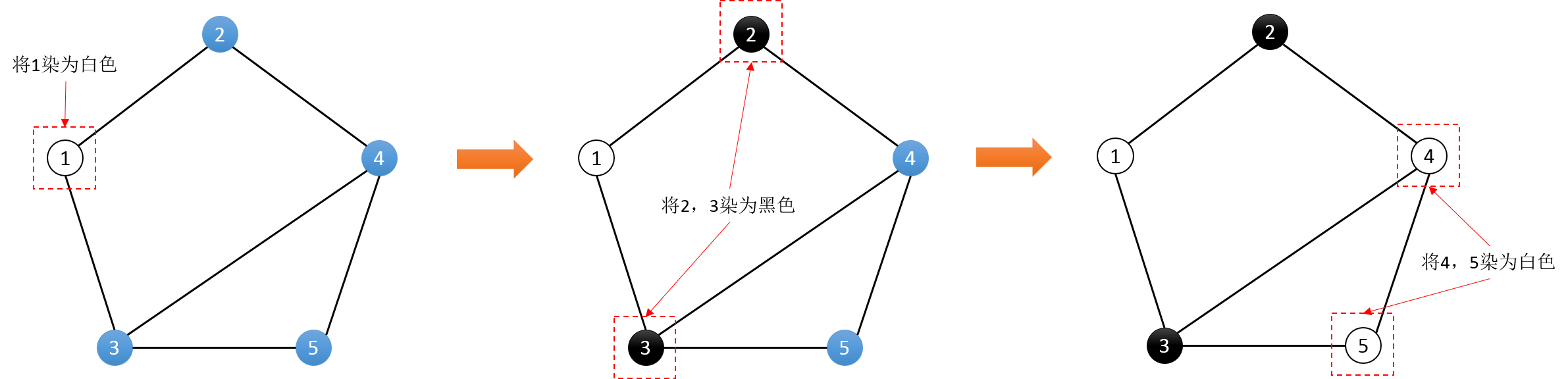
在染色的过程中,我们应该怎样发现错误的记录呢?相信你一定发现了吧。对于一个已经染色的点,如果存在一个与它相邻的已染色点和它的颜色相同,那么就一定存在一条错误 的记录。(如上图的4,5节点)
到此我们就得到了整个图的算法:
- 选取一个未染色的点u进行染色
- 遍历u的相邻节点v:若v未染色,则染色成与u不同的颜色,并对v重复第2步;若v已经染色,如果 u和v颜色相同,判定不可行退出遍历。
- 若所有节点均已染色,则判定可行。
接下来就动手写写吧!
输入
第1行:1个正整数T(1≤T≤10)
接下来T组数据,每组数据按照以下格式给出:
第1行:2个正整数N,M(1≤N≤10,000,1≤M≤40,000)
第2..M+1行:每行两个整数u,v表示u和v之间有一条边
输出
第1..T行:第i行表示第i组数据是否有误。如果是正确的数据输出”Correct”,否则输出”Wrong”
样例输入
2
5 5
1 2
1 3
3 4
5 2
1 5
5 5
1 2
1 3
3 4
5 2
3 5
 copy
copy样例输出
Wrong
Correct
 copy
copy题解
二分图中最简单的题,思路原文中已提到,这里就不赘述了,简单实现的话可以使用二维数组,如果要模拟图的操作的话可以自定义类。
Java
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Queue;
class UndirectedGraphNode {
int label;
int color;
ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode> neighbors;
UndirectedGraphNode(int x) {
this.label = x;
this.color = 0;
this.neighbors = new ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode>();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int T = in.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= T; i++) {
int N = in.nextInt();
int M = in.nextInt();
// initialize graph
List<UndirectedGraphNode> graph = new ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode>();
for (int n = 1; n <= N; n++) {
graph.add(new UndirectedGraphNode(n));
}
// construct graph
for (int j = 1; j <= M; j++) {
int u = in.nextInt(), v = in.nextInt();
graph.get(u - 1).neighbors.add(graph.get(v - 1));
graph.get(v - 1).neighbors.add(graph.get(u - 1));
}
// solve
if (solve(graph)) {
System.out.println("Correct");
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong");
}
}
}
public static boolean solve(List<UndirectedGraphNode> graph) {
// 1 for white, -1 for black, 0 for uncolored
for (UndirectedGraphNode node : graph) {
if (node.color == 0) {
node.color = 1;
Queue<UndirectedGraphNode> q = new LinkedList<UndirectedGraphNode>();
q.offer(node);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int qSize = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < qSize; i++) {
UndirectedGraphNode qNode = q.poll();
for (UndirectedGraphNode neighbor : qNode.neighbors) {
if (neighbor.color == 0) {
neighbor.color = -1 * qNode.color;
q.offer(neighbor);
} else if (neighbor.color + qNode.color != 0) {
// the color of qNode is the same with neighbor
return false;
}
}
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
 copy
copy源码分析
使用 BFS 不容易爆栈。
复杂度分析
时间复杂度 .
