-
Preface
- FAQ
-
Part I - Basics
- Basics Data Structure
- Basics Sorting
- Basics Algorithm
- Basics Misc
-
Part II - Coding
- String
-
Integer Array
-
Remove Element
-
Zero Sum Subarray
-
Subarray Sum K
-
Subarray Sum Closest
-
Recover Rotated Sorted Array
-
Product of Array Exclude Itself
-
Partition Array
-
First Missing Positive
-
2 Sum
-
3 Sum
-
3 Sum Closest
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array II
-
Merge Sorted Array
-
Merge Sorted Array II
-
Median
-
Partition Array by Odd and Even
-
Kth Largest Element
-
Remove Element
-
Binary Search
-
First Position of Target
-
Search Insert Position
-
Search for a Range
-
First Bad Version
-
Search a 2D Matrix
-
Search a 2D Matrix II
-
Find Peak Element
-
Search in Rotated Sorted Array
-
Search in Rotated Sorted Array II
-
Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array
-
Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array II
-
Median of two Sorted Arrays
-
Sqrt x
-
Wood Cut
-
First Position of Target
-
Math and Bit Manipulation
-
Single Number
-
Single Number II
-
Single Number III
-
O1 Check Power of 2
-
Convert Integer A to Integer B
-
Factorial Trailing Zeroes
-
Unique Binary Search Trees
-
Update Bits
-
Fast Power
-
Hash Function
-
Happy Number
-
Count 1 in Binary
-
Fibonacci
-
A plus B Problem
-
Print Numbers by Recursion
-
Majority Number
-
Majority Number II
-
Majority Number III
-
Digit Counts
-
Ugly Number
-
Plus One
-
Palindrome Number
-
Task Scheduler
-
Single Number
-
Linked List
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
-
Remove Duplicates from Unsorted List
-
Partition List
-
Add Two Numbers
-
Two Lists Sum Advanced
-
Remove Nth Node From End of List
-
Linked List Cycle
-
Linked List Cycle II
-
Reverse Linked List
-
Reverse Linked List II
-
Merge Two Sorted Lists
-
Merge k Sorted Lists
-
Reorder List
-
Copy List with Random Pointer
-
Sort List
-
Insertion Sort List
-
Palindrome Linked List
-
LRU Cache
-
Rotate List
-
Swap Nodes in Pairs
-
Remove Linked List Elements
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
-
Binary Tree
-
Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
-
Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
-
Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
-
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
-
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
-
Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
-
Balanced Binary Tree
-
Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum
-
Lowest Common Ancestor
-
Invert Binary Tree
-
Diameter of a Binary Tree
-
Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
-
Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
-
Subtree
-
Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
-
Binary Tree Serialization
-
Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
- Binary Search Tree
- Exhaustive Search
-
Dynamic Programming
-
Triangle
-
Backpack
-
Backpack II
-
Minimum Path Sum
-
Unique Paths
-
Unique Paths II
-
Climbing Stairs
-
Jump Game
-
Word Break
-
Longest Increasing Subsequence
-
Palindrome Partitioning II
-
Longest Common Subsequence
-
Edit Distance
-
Jump Game II
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV
-
Distinct Subsequences
-
Interleaving String
-
Maximum Subarray
-
Maximum Subarray II
-
Longest Increasing Continuous subsequence
-
Longest Increasing Continuous subsequence II
-
Maximal Square
-
Triangle
- Graph
- Data Structure
- Big Data
- Problem Misc
-
Part III - Contest
- Google APAC
- Microsoft
- Appendix I Interview and Resume
-
Tags
Merge Sort - 归并排序
核心:将两个有序对数组归并成一个更大的有序数组。通常做法为递归排序,并将两个不同的有序数组归并到第三个数组中。
先来看看动图,归并排序是一种典型的分治应用。
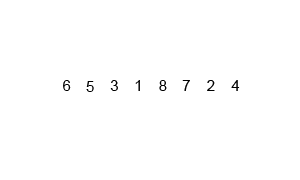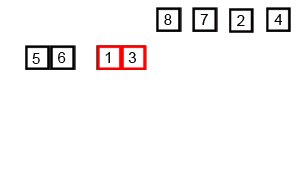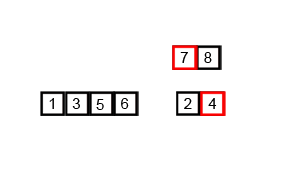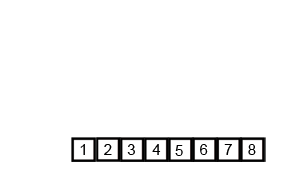
Python
#!/usr/bin/env python
class Sort:
def mergeSort(self, alist):
if len(alist) <= 1:
return alist
mid = len(alist) / 2
left = self.mergeSort(alist[:mid])
print("left = " + str(left))
right = self.mergeSort(alist[mid:])
print("right = " + str(right))
return self.mergeSortedArray(left, right)
#@param A and B: sorted integer array A and B.
#@return: A new sorted integer array
def mergeSortedArray(self, A, B):
sortedArray = []
l = 0
r = 0
while l < len(A) and r < len(B):
if A[l] < B[r]:
sortedArray.append(A[l])
l += 1
else:
sortedArray.append(B[r])
r += 1
sortedArray += A[l:]
sortedArray += B[r:]
return sortedArray
unsortedArray = [6, 5, 3, 1, 8, 7, 2, 4]
merge_sort = Sort()
print(merge_sort.mergeSort(unsortedArray))
 copy
copy原地归并
Java
public class MergeSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int unsortedArray[] = new int[]{6, 5, 3, 1, 8, 7, 2, 4};
mergeSort(unsortedArray);
System.out.println("After sort: ");
for (int item : unsortedArray) {
System.out.print(item + " ");
}
}
private static void merge(int[] array, int low, int mid, int high) {
int[] helper = new int[array.length];
// copy array to helper
for (int k = low; k <= high; k++) {
helper[k] = array[k];
}
// merge array[low...mid] and array[mid + 1...high]
int i = low, j = mid + 1;
for (int k = low; k <= high; k++) {
// k means current location
if (i > mid) {
// no item in left part
array[k] = helper[j];
j++;
} else if (j > high) {
// no item in right part
array[k] = helper[i];
i++;
} else if (helper[i] > helper[j]) {
// get smaller item in the right side
array[k] = helper[j];
j++;
} else {
// get smaller item in the left side
array[k] = helper[i];
i++;
}
}
}
public static void sort(int[] array, int low, int high) {
if (high <= low) return;
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
sort(array, low, mid);
sort(array, mid + 1, high);
merge(array, low, mid, high);
for (int item : array) {
System.out.print(item + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void mergeSort(int[] array) {
sort(array, 0, array.length - 1);
}
}
 copy
copy时间复杂度为 , 使用了等长的辅助数组,空间复杂度为 。
Reference
- Mergesort - Robert Sedgewick 的大作,非常清晰。
