-
Preface
- FAQ
-
Part I - Basics
- Basics Data Structure
- Basics Sorting
- Basics Algorithm
- Basics Misc
-
Part II - Coding
- String
-
Integer Array
-
Remove Element
-
Zero Sum Subarray
-
Subarray Sum K
-
Subarray Sum Closest
-
Recover Rotated Sorted Array
-
Product of Array Exclude Itself
-
Partition Array
-
First Missing Positive
-
2 Sum
-
3 Sum
-
3 Sum Closest
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array II
-
Merge Sorted Array
-
Merge Sorted Array II
-
Median
-
Partition Array by Odd and Even
-
Kth Largest Element
-
Remove Element
-
Binary Search
-
First Position of Target
-
Search Insert Position
-
Search for a Range
-
First Bad Version
-
Search a 2D Matrix
-
Search a 2D Matrix II
-
Find Peak Element
-
Search in Rotated Sorted Array
-
Search in Rotated Sorted Array II
-
Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array
-
Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array II
-
Median of two Sorted Arrays
-
Sqrt x
-
Wood Cut
-
First Position of Target
-
Math and Bit Manipulation
-
Single Number
-
Single Number II
-
Single Number III
-
O1 Check Power of 2
-
Convert Integer A to Integer B
-
Factorial Trailing Zeroes
-
Unique Binary Search Trees
-
Update Bits
-
Fast Power
-
Hash Function
-
Happy Number
-
Count 1 in Binary
-
Fibonacci
-
A plus B Problem
-
Print Numbers by Recursion
-
Majority Number
-
Majority Number II
-
Majority Number III
-
Digit Counts
-
Ugly Number
-
Plus One
-
Palindrome Number
-
Task Scheduler
-
Single Number
-
Linked List
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
-
Remove Duplicates from Unsorted List
-
Partition List
-
Add Two Numbers
-
Two Lists Sum Advanced
-
Remove Nth Node From End of List
-
Linked List Cycle
-
Linked List Cycle II
-
Reverse Linked List
-
Reverse Linked List II
-
Merge Two Sorted Lists
-
Merge k Sorted Lists
-
Reorder List
-
Copy List with Random Pointer
-
Sort List
-
Insertion Sort List
-
Palindrome Linked List
-
LRU Cache
-
Rotate List
-
Swap Nodes in Pairs
-
Remove Linked List Elements
-
Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
-
Binary Tree
-
Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
-
Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
-
Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
-
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
-
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
-
Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
-
Balanced Binary Tree
-
Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum
-
Lowest Common Ancestor
-
Invert Binary Tree
-
Diameter of a Binary Tree
-
Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
-
Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
-
Subtree
-
Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
-
Binary Tree Serialization
-
Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
- Binary Search Tree
- Exhaustive Search
-
Dynamic Programming
-
Triangle
-
Backpack
-
Backpack II
-
Minimum Path Sum
-
Unique Paths
-
Unique Paths II
-
Climbing Stairs
-
Jump Game
-
Word Break
-
Longest Increasing Subsequence
-
Palindrome Partitioning II
-
Longest Common Subsequence
-
Edit Distance
-
Jump Game II
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV
-
Distinct Subsequences
-
Interleaving String
-
Maximum Subarray
-
Maximum Subarray II
-
Longest Increasing Continuous subsequence
-
Longest Increasing Continuous subsequence II
-
Maximal Square
-
Triangle
- Graph
- Data Structure
- Big Data
- Problem Misc
-
Part III - Contest
- Google APAC
- Microsoft
- Appendix I Interview and Resume
-
Tags
Insertion Sort - 插入排序
核心:通过构建有序序列,对于未排序序列,在已排序序列中从后向前扫描(对于单向链表则只能从前往后遍历),找到相应位置并插入。实现上通常使用in-place排序(需用到O(1)的额外空间)
- 从第一个元素开始,该元素可认为已排序
- 取下一个元素,对已排序数组从后往前扫描
- 若从排序数组中取出的元素大于新元素,则移至下一位置
- 重复步骤3,直至找到已排序元素小于或等于新元素的位置
- 插入新元素至该位置
- 重复2~5
性质:
- 交换操作和数组中倒置的数量相同
- 比较次数>=倒置数量,<=倒置的数量加上数组的大小减一
- 每次交换都改变了两个顺序颠倒的元素的位置,即减少了一对倒置,倒置数量为0时即完成排序。
- 每次交换对应着一次比较,且1到N-1之间的每个i都可能需要一次额外的记录(a[i]未到达数组左端时)
- 最坏情况下需要
N^2/2次比较和N^2/2次交换,最好情况下需要N-1次比较和0次交换。 - 平均情况下需要
N^2/4次比较和N^2/4次交换
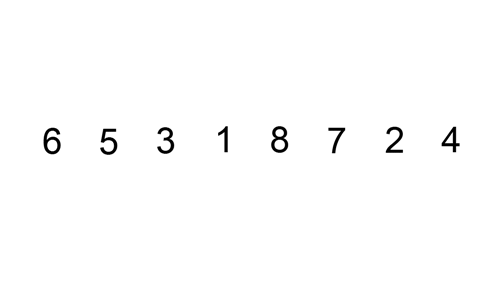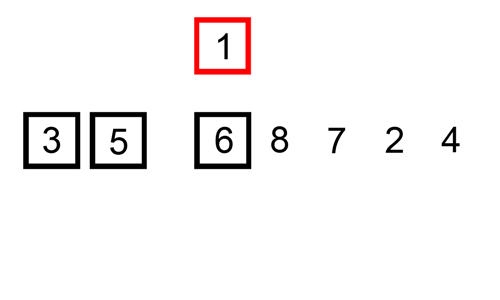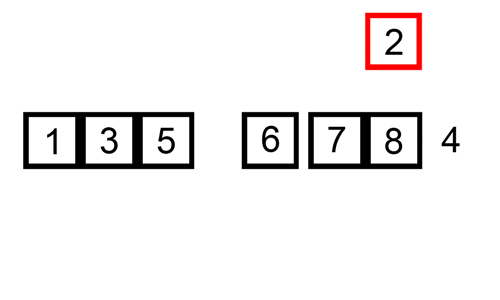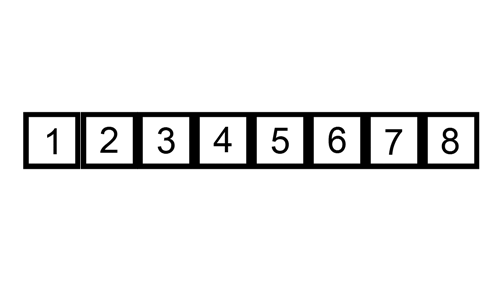
Implementation
Python
#!/usr/bin/env python
def insertionSort(alist):
for i, item_i in enumerate(alist):
print alist
index = i
while index > 0 and alist[index - 1] > item_i:
alist[index] = alist[index - 1]
index -= 1
alist[index] = item_i
return alist
unsorted_list = [6, 5, 3, 1, 8, 7, 2, 4]
print(insertionSort(unsorted_list))
 copy
copyJava
public class Sort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int unsortedArray[] = new int[]{6, 5, 3, 1, 8, 7, 2, 4};
insertionSort(unsortedArray);
System.out.println("After sort: ");
for (int item : unsortedArray) {
System.out.print(item + " ");
}
}
public static void insertionSort(int[] array) {
int len = array.length;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
int index = i, array_i = array[i];
while (index > 0 && array[index - 1] > array_i) {
array[index] = array[index - 1];
index -= 1;
}
array[index] = array_i;
/* print sort process */
for (int item : array) {
System.out.print(item + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
 copy
copy实现(C++):
template<typename T>
void insertion_sort(T arr[], int len) {
int i, j;
T temp;
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
temp = arr[i];
for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0 && arr[j] > temp; j--) {
a[j + 1] = a[j];
}
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
 copy
copy希尔排序
核心:基于插入排序,使数组中任意间隔为h的元素都是有序的,即将全部元素分为h个区域使用插入排序。其实现可类似于插入排序但使用不同增量。更高效的原因是它权衡了子数组的规模和有序性。
实现(C++):
template<typename T>
void shell_sort(T arr[], int len) {
int gap, i, j;
T temp;
for (gap = len >> 1; gap > 0; gap >>= 1)
for (i = gap; i < len; i++) {
temp = arr[i];
for (j = i - gap; j >= 0 && arr[j] > temp; j -= gap)
arr[j + gap] = arr[j];
arr[j + gap] = temp;
}
}
 copy
copy